Stochastic Resonance emergence from a Minimalistic Behavioral Rule
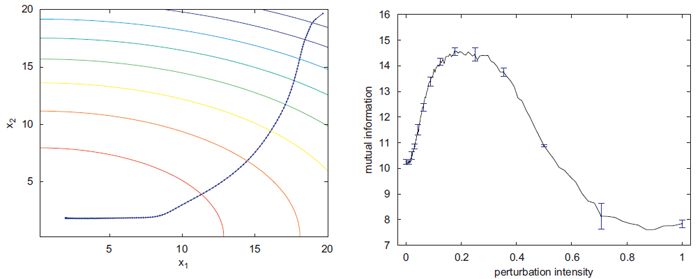
The behavioral rule we propose can be formalized in a straightforward manner in a completely general way as well. Denoting by uit the i-th component of a motor command of an agent at time t, the same component at time t+1 is given by

where R is a random variable such as a white gaussian noise, ηi means the intensity of the noise in the i-th component of the motor command, and ΔAt expresses how much the agent improved its state during the t-th time step.
We have confirmed and theoretically proven that the agent can follow a gradient of an evaluation function despite that the rule is extremely simple thanks to stochastic resonance.
Reference
- Shuhei Ikemoto, Fabio DallaLibera, Koh Hosoda, and Hiroshi Ishiguro, "Minimalistic Behavioral Rule derived from Bacterial Chemotaxis in a Stochastic Resonance Setup", Physical Review E: Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, Vol. 85, No. 2, pp. 021905, 2012.
- Shuhei Ikemoto, Fabio DallaLibera, and Hiroshi Ishiguro, "Stochastic Resonance Emergence from a Minimalistic Behavioral Rule", Journal of Theoretical Biology, Vol. 273, No. 1, pp. 179-187, 2011.