 |
 |
 |
[ ���n�����V�X�e���̍\�z�ƃf�o�C�X�� ] |
 |
 |
�T�u�v���W�F�N�g���[�_�[�F�� |
|
 |
|
 |
 |
�C�n��͕킵�����n�����V�X�e���̍\�z�ƃf�o�C�X��
| �i�P�j |
�T�u�v���W�F�N�g�̊T�v
�C�n�͋�ԔF�m��ꏊ�̎��n��w�K�@�\�����B�{�T�u�v���W�F�N�g�̖ړI�́A���̂悤�ȊC�n�̋@�\�Ƀq���g���@���A���^�C���������o�V�X�e���ƇA���[�J���i�r�Q�[�V�����V�X�e���������J�����邱�Ƃł���B
 |
�y���A���^�C���������o�V�X�e���z
�����̐M�����C�n�̃��J�����g�l�b�g���[�N�̈قȂ�ꏊ�ɉ����ƁA�����̐M���̓��̓^�C�~���O�Ɉˑ����ăj���[���������̓`�d���_�C�i�~�J���ȋ�ԃp�^�[����������i�}1a�j[1-3]�B���̐�����p����ƁA�M���̏������o�Ɗw�K���\�ł���[4-5]�B�����̓��͐M�������n��ŕ��ԉ摜�ƍl����Ɖ摜���̕��̂̓��������o���邱�Ƃ��ł���B�{�T�u�v���W�F�N�g�ł́A�}1b�Ɏ����悤�ȁA���̂̈ʒu�A�ړ������A����ё��x���Ɍ��o�ł��镨�̂̓������o�A���S���Y����]���f������̗ь������ŊJ������[6-8]�B����ɁA�]���f������̗ь������ƃf�o�C�X����̐_���������Ƃ̋����ŁA���̓������o�V�X�e���̏o�̓p�^�[����p���A�l�Ԃ̒m���Ɋ�Â����t�@�W�B���_�ɂ��O���̕��̂Ƃ̏Փˊ댯�x��������������i�}1c�j[11]�B���̃A���S���Y���͕����A���S���Y���ł���A�W�ω�H���ɂ�郊�A���^�C���������\�ł���B���̃A���S���Y���ɏ]���āA�]���f������̗ь������ƃf�o�C�X����̐X�]�������Ƃ̋����ŁA���̂̓������o�̂��߂̃f�W�^��LSI�A�[�L�e�N�`�����l�Ă��AFPGA�Ɏ��������i�}1d�j[9-11]�B�����̃V�X�e���������ړ����{�b�g�gWITH�h�ɓ��ڂ��A���ʏՓˁA�I�t�Z�b�g�Փ˂Ȃǂɑ������s���������邱�Ƃ��ł����i�}1e�j[11]�B�����Ԃœ��삷��{�V�X�e���́A�����Ԃ̏Փ˖h�~���ɗL���ł���B
|
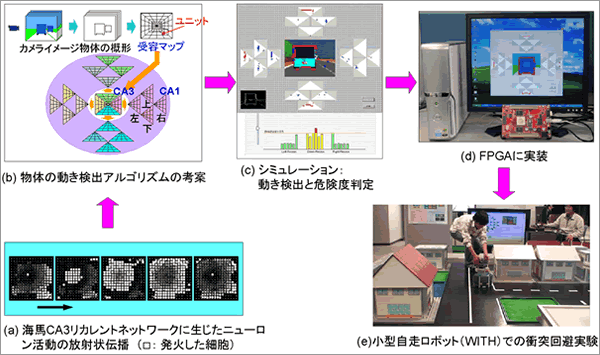 |
| �}�P�@�C�n�̋@�\�Ƀq���g���������o�V�X�e���ƏՓˉ�� |
 |
�y���[�J���i�r�Q�[�V�����V�X�e���z
��ԏ���S�����o�M���ɂ���āA�k���玿����C�n��ʂ��Ěk���玿�ɖ߂郋�[�v������I��I�ɋ������邱�Ƃ��ł���i�}2a�j�B���̌��ʁA�k���玿�̏ꏊ�זE������Ȃ��ɂȂ�A�ꏊ�̎��n�w�K�L�������i�}2b�j[12-15]�B���̃��[�v��H�\���Ǝ��n��w�K�@�\�̎d�g�݂Ƀq���g�āA�]���f������̗ь������ƃf�o�C�X����̐_���������Ƃ̋����ŁA���[�J���i�r�Q�[�V�����V�X�e���������J������[16]�B���̃V�X�e���́A�J�����摜����K�ɒ��o���������h�}�[�N�̎��n������[�g���Ƃ��ċL�����A���̃����h�}�[�N���琬�郍�[�J�����[�g���Ɋ�Â��������I�i�r�Q�[�V���������s�ł���B���̃V�X�e���̐S�����ł��郍�[�J�����[�g�L�����j�b�g�i�}2c�j�ɋL�����ꂽ���[�g���́A�Ď��s�Ō��o���ꂽ�����h�}�[�N���n��Ɣ�r����A�����ȕω����F�߂�ꂽ�ꍇ�͓K������悤�ɂȂ��Ă���B���̃��[�J���i�r�Q�[�V�����V�X�e���̗L�����ɂ��ẮA�����ړ����{�b�g�gWITH�h��p���Ċm���߂��i�}2d�j�B�{���[�J���i�r�Q�[�V�����V�X�e���́A���m�̋�Ԃł̎����I���[�g�w�K�⎩�����s�����\�ɂ���Ɗ��҂����B
|
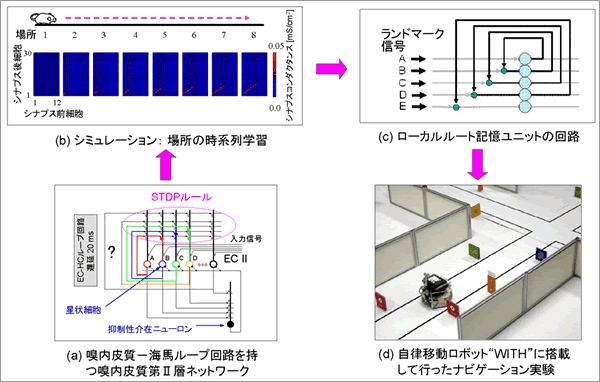 |
| �}�Q�@�C�n�̋@�\�Ƀq���g�����[�J���i�r�Q�[�V�����V�X�e�� |
|
 |
| �i�Q�j |
�\�������o�[�Ɩ������S
| �T�u�v���W�F�N�g���[�_�[ |
 |
�� ���j�i�]���f������j |
�F |
�C�n�̋@�\�Ƀq���g�����̂̓������o�A���S���Y���ƃ��[�J���i�r�Q�[�V�����A���S���Y���̍l�� |
| ���S�� |
 |
�X�] ���i�f�o�C�X����j |
�F |
���̂̓������o�A���S���Y���̃n�[�h�E�F�A���A�V�X�e���\�z�A�����ړ����{�b�g�ւ̎��� |
 |
�_�� �i�f�o�C�X����j |
�F |
�t�@�W�B���_�ɂ��Փˊ댯�x����A���[�J���i�r�Q�[�V�����A���S���Y���l�ĂƃV�X�e���\�z�A�����ړ����{�b�g�ւ̎��� |
 |
���c ��I�i�f�o�C�X����j |
�F |
���̂̓������o�A���S���Y���̃n�[�h�E�F�A���A�V�X�e���\�z�A�����ړ����{�b�g�ւ̎��� |
|
 |
|
 |
| �����Ɛу��X�g |
| [1] |
M. Yoshida, H. Hayashi, Regulation of spontaneous rhythmic activity and organization of pacemakers as memory traces by spike-timing-dependent synaptic plasticity in a hippocampal model, Physical Review E, Vol. 69, pp. 011910-1�`011910-15, 2004.
|
| [2] |
H. Hayashi, M. Yoshida, A memory model based on dynamical behavior of the hippocampus, Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Knowledge-Based Intelligent Information and Engineering Systems, Part 1, pp. 967-973, 2004.
|
| [3] |
H. Hayashi, M. Yoshida, A memory model of the hippocampus for the foundation of brain-inspired information technology, International Congress Series, Vol. 1269, pp. 109-112, 2004.
|
| [4] |
M. Yoshida, H. Hayashi, Organization of cell assemblies that code temporal sequences in a hippocampal CA3-CA1 model, Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, pp.495-500, 2004.
|
| [5] |
M. Yoshida, H. Hayashi, Emergence of sequence sensitivity in a hippocampal CA3-CA1 model, Neural Networks, Vol. 20, No. 6, pp. 653-667, 2007.
|
| [6] |
�� �C���A�X�]���A���R�_�V�A���c��I�A�� ���j�A�C�n���n�������f���Ɋ�Â��ړ��̌��o��@�̃f�W�^��LSI�A�[�L�e�N�`���A��5����Ȋw�Z�p�t�H�[�����App. 59-61, 2006.
|
| [7] |
H. Hayashi, K. Nakada, T. Morie, A Moving object detection algorithm inspired by the sequence detection in the hippocampus and its digital LSI implementation, International Congress Series Vol. 1301, pp. 35-38, 2007.
|
| [8] |
�� ���j�APTC�o��A2006�A�č��AEP�A�؍��A���{�Ɉڍs�ς�
|
| [9] |
H. Liang, H. Nakayama, K. Nakada, T. Morie, H. Hayashi, Digital VLSI implementation of a moving object detection algorithm based on neural propagation in the hippocampus, Proceedings of the International Symposium on Intelligent Signal Processing and Communication Systems, pp. 614-617, 2006.
|
| [10] |
H. Liang, T. Morie, H. Nakayama, K. Nakada, H. Hayashi, An FPGA-based real-time moving-object detection system based on neuronal propagation in the hippocampus, Proceedings of the International Workshop on Nonlinear Circuits and Signal Processing, pp.509-512, 2007.
|
| [11] |
H. Liang, T. Morie, Y. Suzuki, K. Nakada, T. Miki, H. Hayashi, An FPGA-based collision warning system using hybrid approach, Proceedings of the International Conference on Hybrid Intelligent Systems, pp.30-35, 2007.
|
| [12] |
J. Igarashi, M. Yoshida, K. Tateno, H. Hayashi, Synchronized subthreshold oscillations and phase coding in a network model of the entorhinal cortex, Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, pp.3119-3124, 2004.
|
| [13] |
J. Igarashi, H. Hayashi, K. Tateno, Theta phase coding in entorhinal-hippocampal loop circuits organized by afferent signals, Proceedings of the International Symposium on Nonlinear Theory and its Applications, pp.595-598, 2006.
|
| [14] |
J. Igarashi, K. Tateno, H. Hayashi, Phase coding by organization of entorhinal cortex-hippocampus loop circuits, International Congress Series, Vol. 1291, pp. 117-120, 2006.
|
| [15] |
J. Igarashi, H. Hayashi, K. Tateno, Theta phase coding in a network model of the entorhinal cortex layer II with entorhinal-hippocampal loop connections, Cognitive Neurodynamics, Vol. 1, Issue 2, pp. 169-184, 2007.
|
| [16] |
T. Miki, H. Hayashi, Y. Goto, T. Inoue, M. Watanabe, Practical Local Navigation System Based on Entorhino-hippocampal Functions, Proceedings of Joint 4th International Conference on Soft Computing and Intelligent Systems and 9th International Symposium on advanced Intelligent Systems, pp.1783-1787, 2008.
|
|
|
|