Development of Musculoskeletal Robot Arms
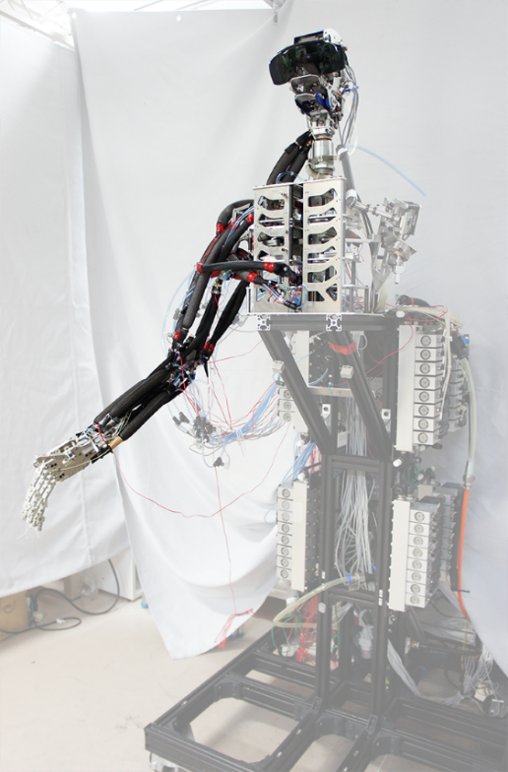
Human's musculoskeletal structures are very complex and they look problems that make their control very difficult in terms of robotics. In this research, we however assume that their musculoskeletal structure must have advantages to realize highly sophisticated human's motions because they have been optimized throughout evolution. In particular, we are focusing on the superior limb and developing musculoskeletal robot arms to reveal and exploit their unknown functions.
Reference
- Arne Hitzmann, Hiroaki Masuda, Shuhei ikemoto, and Koh Hosoda, "Anthropomorphic Musculoskeletal ten degrees-of-freedom Robot Arm driven by Pneumatic Artificial Muscles", Advanced Robotics, Vol. 32, Issue 15, pp. 865-878, 2018.
- Koh Hosoda, Shunsuke Sekimoto, Yoichi Nishigori, Shinya Takamuku, and Shuhei Ikemoto, "Anthropomorphic Muscular-Skeletal Robotic Upper Limb For Understanding Embodied Intelligence", Advanced Robotics, Vol. 26, No. 7, pp. 729-744, 2012.